HEAD & nECK
Thyroidectomy
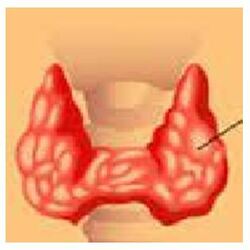
The butterfly-shaped gland located in the front of the neck is known as thyroid. It generates hormones that control the process of metabolism, including the heart rate to burning calories.
A thyroidectomy is the surgical removal of the complete thyroid gland. It often performed by endocrine surgeons or head and neck surgeons perform a thyroidectomy when a patient is diagnosed for thyroid cancer or some other condition of the thyroid gland or Goiter.
Parotidectomy
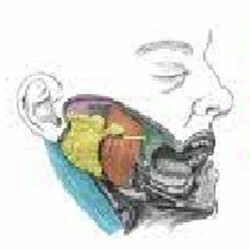
A parotidectomy is the surgical excision (removal) of the parotid gland, the major and largest of the salivary glands. The procedure is most typically performed due to neoplasms (tumors), which are growths of rapidly and abnormally dividing cells. Neoplasms can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). The majority of parotid gland tumors are benign, however 20% of parotid tumors are found to be malignant. Parotidectomy is performed mostly by oral and maxillofacial surgeon and ENT surgeon.
Types of Parotidectomy
- Extracapsular dissection – excision of the parotid tumor surrounded by some millimetres of healthy tissue, without searching and exposing the main truck of the facial nerve.
- Superficial (near surface) or lateral (side) parotidectomy – excising all the parts of the gland superficial or lateral to the facial nerve.
Partial superficial parotidectomy – superficial parotidectomy where the surgeon excises only the portion of the gland surrounding the neoplasm. Only some nerves of the face are dissected during this procedure.
Formal superficial parotidectomy – superficial parotidectomy where the cervicofacial and temporofacial nerves are dissected.
- Total parotidectomy– total removal of the deep part of the parotid gland. Typically performed if neoplasm is affecting deep part of parotid gland. Surgeon tries to remove the gland apart from the facial nerve, yet dissecting all branches of the facial nerves. This method can be done using the transcervical surgical approach. Transcervical approach – less invasive procedure that involves cutting only a small incision in the neck.
- Radical parotidectomy – Typically performed if malignant neoplasm is impinging on facial nerve. Facial nerve excised in addition to parotid gland.
Excisional biopsy Neck
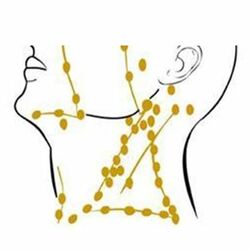
Our body comprises of small organs called lymph nodes and are the part of the immune system. They are located throughout the body and connected to each other by lymph vessels.
There are many such Neck lymph nodes present in the neck.
These sometimes enlarge, due to infection, however cancer could also be the cause of this enlargement.
Several tests like to such as a needle biopsy are conducted to diagnose cancer. But sometimes, the diagnosis needs more information to identify e the underlying cause.
This process of removal of the enlarged lymph node, for the tissue to be sent to the lab is known as Excisional biopsy.
Branchial cleft cyst
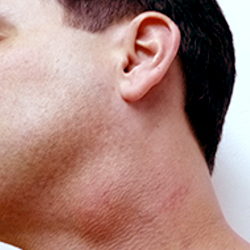
A branchial cleft cyst is a congenital abnormality that forms when remnants of the branchial cleft, which is a structure that develops in the embryo and typically disappears before birth, persist and develop into a fluid-filled sac in the neck. These cysts are typically benign and may not cause symptoms, but can become infected or enlarge and cause pain or discomfort. Branchial cleft cysts are most commonly diagnosed in children or young adults, and are typically located on one side of the neck. Diagnosis is typically made through physical examination and imaging studies such as ultrasound or CT scan. Treatment for a branchial cleft cyst typically involves surgical removal of the cyst and its associated tract to prevent recurrence.